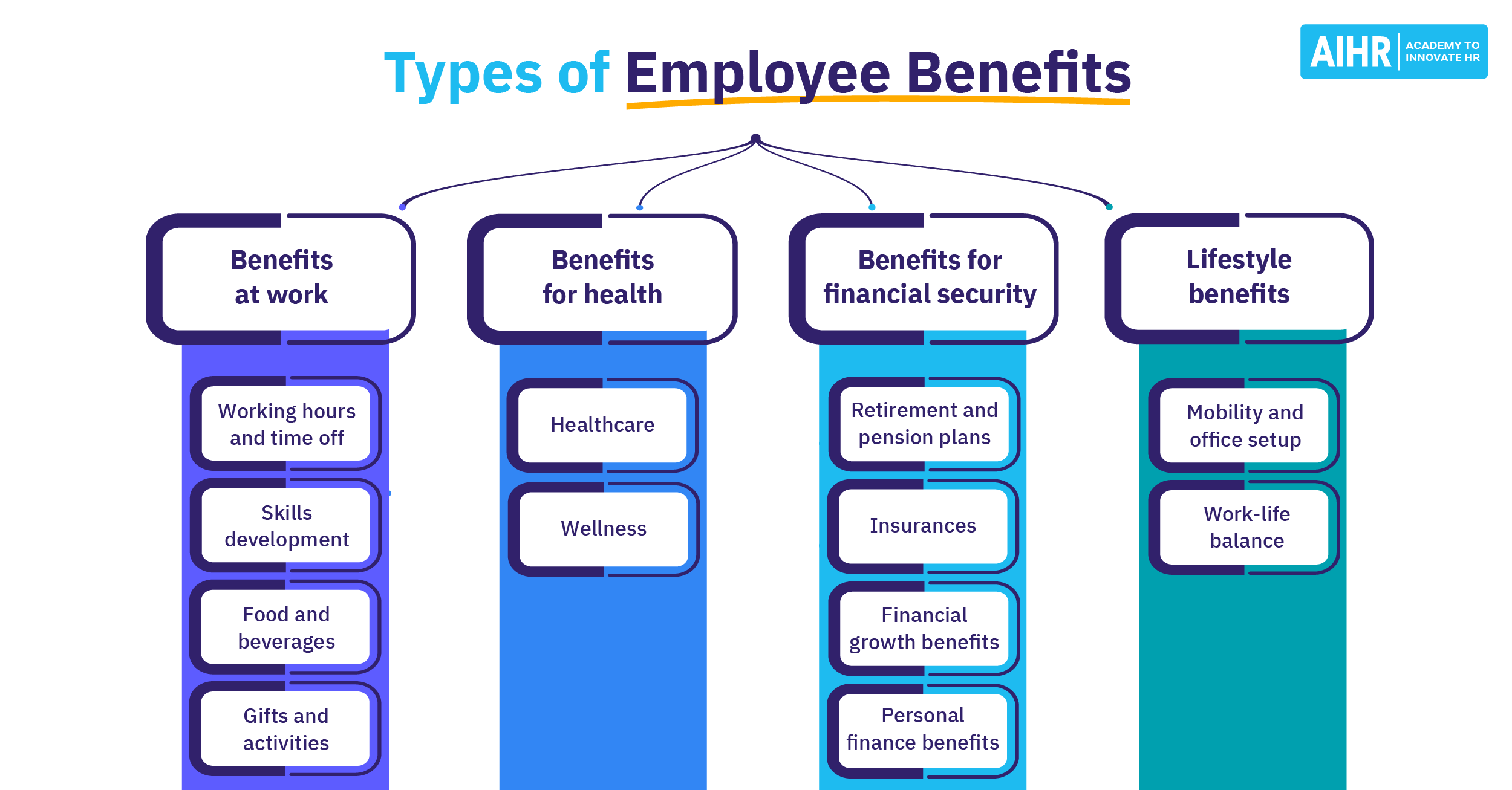
Group health insurance offered through employers is a popular and valuable option for many individuals seeking comprehensive and cost-effective healthcare coverage. Employer-sponsored plans provide a range of benefits that can make health insurance more accessible and affordable. Here’s a comprehensive guide to understanding and exploring group health insurance options through employers.

1. What is Group Health Insurance?
Group health insurance is a type of coverage provided by an employer to a group of employees. It typically offers comprehensive health benefits at a lower cost compared to individual plans due to the collective bargaining power of the group. The employer usually negotiates the terms and cost of the plan with insurance providers, which often results in lower premiums and better coverage options for employees.
2. Advantages of Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
There are several key benefits to obtaining health insurance through an employer:
- Cost Savings: Employers often cover a portion of the premium costs, making the insurance more affordable for employees. In some cases, employers may offer to cover a significant portion or the entire premium.
- Lower Premiums: Group plans generally have lower premiums than individual health insurance plans because the risk is spread across a larger group of people.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Employer-sponsored plans often provide a broad range of benefits, including preventive care, hospital visits, prescription drugs, and mental health services.
- Convenience: Enrollment in group health insurance is usually straightforward and often automatic, with options to add dependents and make changes during open enrollment periods.
3. Types of Employer-Sponsored Plans
Employers may offer various types of health insurance plans, including:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): HMO plans require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) and obtain referrals to see specialists. These plans often have lower premiums and out-of-pocket costs but require you to use a network of doctors and hospitals.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPO plans offer more flexibility in choosing healthcare providers and do not require referrals for specialists. They typically have higher premiums but offer broader network options.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): EPO plans are similar to PPOs but do not cover any out-of-network care except in emergencies. They usually have lower premiums compared to PPOs.
- Point of Service (POS): POS plans combine features of HMO and PPO plans. Members choose a PCP and need referrals for specialists, but can also see out-of-network providers at a higher cost.
- High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): HDHPs have higher deductibles but lower premiums. They are often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) to help save for out-of-pocket expenses.
4. Enrollment and Eligibility
Eligibility for employer-sponsored health insurance typically depends on your employment status and tenure:

- Full-Time vs. Part-Time: Most employers offer health insurance to full-time employees. Part-time employees may be eligible depending on the employer’s policy.
- Waiting Periods: Some employers have waiting periods before new employees can enroll in health insurance. This period can vary, often ranging from 30 to 90 days.
- Open Enrollment: Employees can usually enroll in or change their health insurance plans during the open enrollment period, which typically occurs once a year. Special enrollment periods may also be available for life events such as marriage, birth of a child, or changes in employment status.
5. Cost Sharing
While employers often subsidize the cost of premiums, employees are usually responsible for some cost-sharing elements:
- Premiums: Employees pay a portion of the monthly premium through payroll deductions.
- Deductibles: The amount you must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance plan begins to cover costs.
- Copayments and Coinsurance: Fixed amounts (copayments) or percentages (coinsurance) you pay for specific services and medications.
6. Evaluating Your Options
When exploring group health insurance options, consider the following factors:
- Coverage Needs: Assess your healthcare needs, including any ongoing treatments or medications, to ensure the plan covers necessary services.
- Network Providers: Check if your preferred doctors and hospitals are included in the plan’s network.
- Plan Costs: Compare premiums, deductibles, and out-of-pocket costs to find a plan that fits your budget.
- Additional Benefits: Look for additional features such as wellness programs, mental health services, and telemedicine options.
7. Seeking Assistance
If you have questions or need help navigating your employer’s health insurance options, consider the following resources:
- Human Resources Department: Your HR team can provide detailed information about the available plans, enrollment procedures, and answer any questions you may have.
- Benefits Counselors: Some employers offer access to benefits counselors who can help you understand your options and make informed decisions.
- Online Tools: Many employers provide online tools and resources to compare plan options and estimate costs.
Conclusion
Exploring group health insurance options through your employer offers significant benefits, including cost savings, comprehensive coverage, and convenience. By understanding the types of plans available, evaluating your needs, and using available resources, you can make informed decisions about your health insurance. Employer-sponsored health insurance is a valuable benefit that can help manage healthcare costs and provide peace of mind for you and your family.